Table of Contents
- What Is the Google Chrome Approximate Location Feature?
- Why Google Is Introducing Approximate Location in Chrome
- How the New Location Toggle Works in Chrome for Android
- Privacy Advantages & User Control Improvements
- How to Enable the Feature Early (Chrome Flags)
- Comparison With Other Browsers & Android’s System-Level Controls
- Industry Impact: What It Means for Developers & Websites
- Chrome’s Recent UI Refresh & Material 3 Design Updates
- Conclusion: The Future of Location Privacy on Android
What Is the Google Chrome Approximate Location Feature?
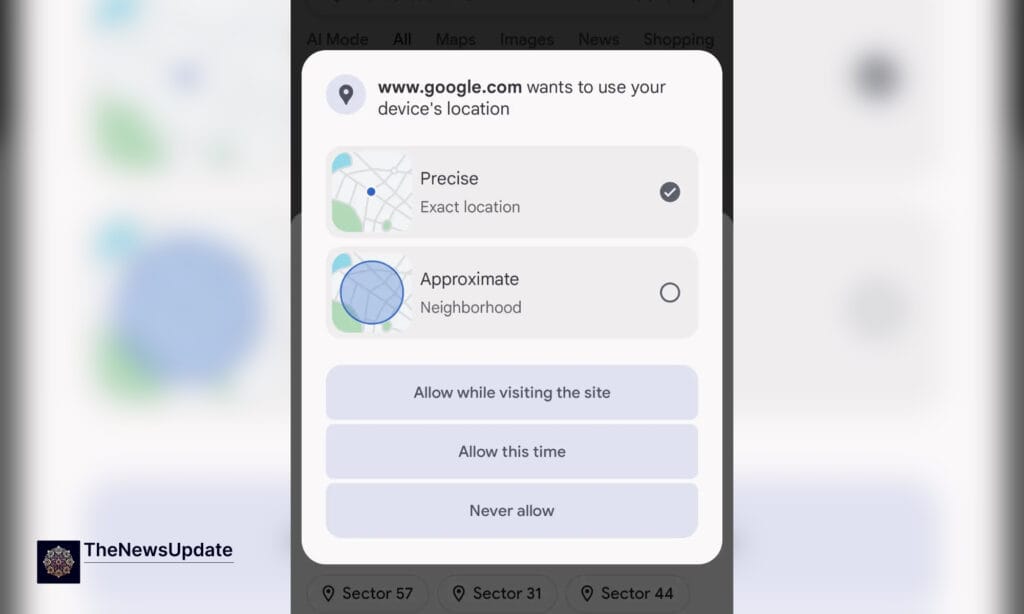
The Google Chrome Approximate Location Feature is a newly tested capability that allows users to choose whether a website receives their exact GPS coordinates or a less precise, generalized location. This update is significant because Chrome has long relied on binary permissions—either giving full precise location or none at all. With the introduction of an approximate toggle, Chrome aligns itself with modern privacy expectations where users demand granular control over their data.
According to early reports, Chrome for Android version 142.0.7444.171 includes an updated permission dialog that displays two options:
- Precise Location – Shares accurate GPS-level coordinates.
- Approximate Location – Shares a general region, city-level, or neighborhood-level location only.
This new feature gives Android users the ability to protect sensitive data while still allowing websites to function normally for services that do not require precision.
Why Google Is Introducing Approximate Location in Chrome
Google’s decision to test the Google Chrome Approximate Location Feature reflects a broader industry shift toward stronger user privacy protections. Over the past decade, concerns about data tracking, behavioral profiling, and surveillance have grown exponentially. Companies like Apple popularized approximate location features at the OS level, and now Google aims to bring similar flexibility directly inside Chrome.
There are three major reasons behind this move:
- Growing privacy concerns: Users increasingly distrust websites that request precise location without justification.
- Regulatory pressure: Global laws like GDPR and CCPA encourage minimal data collection.
- Consumer control: Modern users want to pick and choose exactly what data they share.
By adding the approximate location toggle, Chrome becomes more aligned with user expectations and positions itself as a privacy-first browser.
How the New Location Toggle Works in Chrome for Android
When a website requests your location, Chrome now displays a redesigned permission window. Instead of automatically granting precise access at the app level, Chrome lets users select how much detail a website receives. This provides:
- Flexible privacy controls
- Website-specific location settings
- Reduced risk of unnecessary data exposure
For example, a weather website that only needs city-level context will receive approximate data, while navigation services like Google Maps can still request precise coordinates.

Early testers say the UI now includes an icon-based horizontal permission prompt with clear descriptions. This makes it easier for everyday users to understand what they are sharing.
Privacy Advantages & User Control Improvements
The Google Chrome Approximate Location Feature offers a significant set of privacy advantages. Today, many websites attempt to infer details about users even without direct GPS access. Providing approximate location ensures:
- Reduced ability for websites to track users across sessions
- Better protection against fingerprinting and profiling
- More transparency around data usage
- Improved browsing safety for vulnerable communities and minors
Users benefit the most because they finally gain fine-grained control over each site’s access. Previously, users had to either disable location entirely or accept full access. This new approach brings Chrome closer to Android’s system-level privacy philosophy.
How to Enable the Feature Early (Chrome Flags)
Although Google is A/B testing the feature and has not released it publicly, users can activate it manually through Chrome Flags. Here’s how:
- Open Chrome on Android.
- Type chrome://flags in the address bar.
- Search for Approximate Geolocation Permission.
- Select: Enable – Prompt arm: Horizontal with Icon + Description.
- Restart Chrome to apply the changes.
After enabling it, websites requesting location will show the updated permission interface.
Comparison With Other Browsers & Android’s System-Level Controls
Android already allows apps to choose between approximate and precise location. However, Chrome’s new feature works at the website level, not the app level. This doubles the protection:
- App-level control: Determines what Chrome can access.
- Website-level control: Determines what sites inside Chrome can access.
Safari and Firefox provide robust privacy features, but Chrome’s upcoming toggle offers finer control than either browser currently provides. This update will likely push competitors to reevaluate their own permission frameworks.
Industry Impact: What It Means for Developers & Websites
Developers will be significantly affected by the Google Chrome Approximate Location Feature. Websites that need precise data—such as delivery apps, mapping tools, ride-sharing platforms, or hyper-local services—will need to explicitly justify why precision is required. Otherwise, they will receive only general location information.
For some websites, this change improves performance. By receiving only approximate data, they can avoid unnecessary location processing and reduce power consumption. At the same time, privacy compliance becomes easier since the site adheres to data-minimization principles.
Chrome’s Recent UI Refresh & Material 3 Design Updates
Alongside the approximate location update, Chrome version 141 introduced a visual refresh inspired by Google’s Material 3 Expressive design language. These UI changes include:
- A redesigned three-dot menu
- A modernized Bookmark icon
- Smoother animations and rounded elements
- Improved readability and accessibility
These design refinements signal Google’s focus on consistency across Android apps while making Chrome feel more intuitive and up-to-date. Many users have already received the update through a server-side rollout.
Conclusion: The Future of Location Privacy on Android
The Google Chrome Approximate Location Feature represents a major step forward for mobile privacy. As data concerns grow worldwide, Google’s move to empower users with more precise controls reflects the future of digital browsing. While the company has not confirmed a public rollout date, early testing shows that Android users will soon enjoy a safer, more flexible web experience.
Related Reads
By The News Update— Updated November 2025