ByteDance AI phone, the parent company of TikTok, recently made headlines by demonstrating a smartphone that could nearly operate itself using artificial intelligence. The Nubia M153 prototype in China showcased the company’s Doubao AI agent performing tasks autonomously, raising excitement about the future of AI-powered devices. However, privacy concerns quickly emerged, forcing ByteDance to limit the phone’s capabilities.
The Rise of Fully Agentic AI Smartphones
The Nubia M153 is described as a fully agentic smartphone, meaning its AI can act on behalf of users with minimal input. Unlike traditional voice assistants such as Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant, which rely on voice commands and app-level APIs, the Nubia M153’s Doubao AI can perceive the screen, understand goals, and navigate apps directly to complete tasks. In demonstrations, the AI successfully performed multi-step actions such as booking tickets, typing messages, making calls, and even managing payments.
Tech enthusiasts and AI researchers alike have been intrigued by the phone’s capabilities. The system, described as a full-stack AI, interacts directly with the operating system instead of being restricted to app-level functions. This enables the AI to handle complex, cross-app workflows autonomously, something not yet achievable by mainstream consumer devices.
How Doubao AI Works ByteDance AI phone
The AI-powered Nubia M153 integrates ByteDance’s in-house large language model ecosystem, Doubao, with a customized Android operating system. Doubao functions as a personal assistant that can visually interpret the phone’s interface, understand the user’s goals, and execute tasks independently. This allows the AI to operate like a human user, tapping, scrolling, typing, and navigating multiple apps seamlessly.
For instance, a user could instruct Doubao to book a train ticket, and the AI would determine which apps to use, enter all required information, and finalize the transaction without further guidance. Unlike conventional assistants, this autonomous functionality does not rely on pre-defined scripts or commands, representing a new frontier in mobile AI.
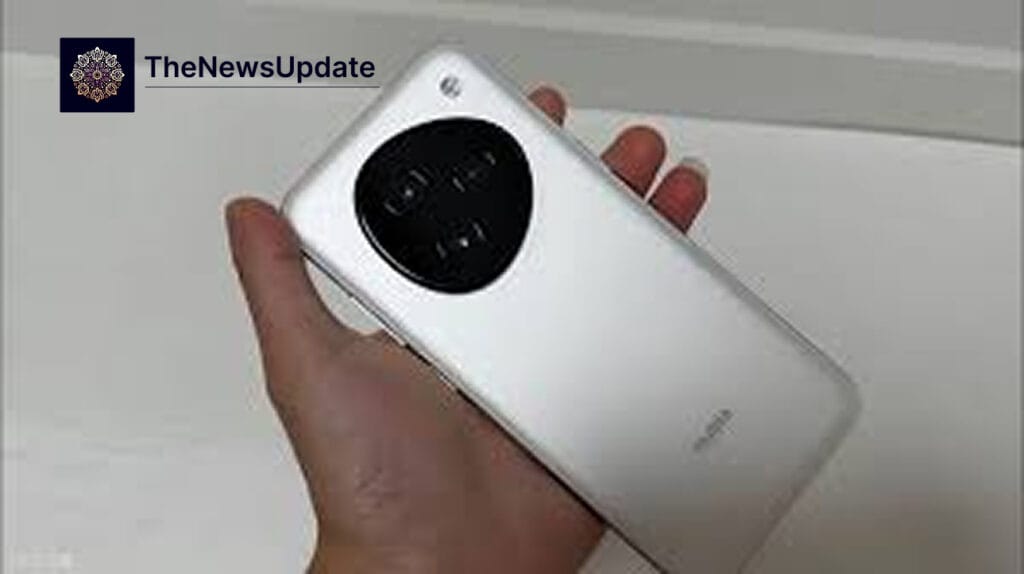

Privacy Concerns Prompt a Quick Response
Despite the impressive capabilities, ByteDance’s AI smartphone faced immediate scrutiny over privacy risks. The AI’s ability to see everything on the screen, access personal messages, and interact with sensitive information raised alarm among experts and the public. Critics argued that giving an AI complete control over a device could expose users to unprecedented security and data risks.
Responding to the backlash, ByteDance reportedly scaled back Doubao’s permissions, limiting its access to sensitive functions until additional safeguards are implemented. The company framed this move as a precautionary measure rather than a full retreat, emphasizing its commitment to safety while continuing to develop agentic AI features.
The Tension Between Innovation and Trust
The Nubia M153 experiment highlights a growing tension in the tech industry between advancing AI capabilities and maintaining user trust. As AI systems become more autonomous, companies face the challenge of balancing innovation with privacy and security. ByteDance’s quick adjustment demonstrates the need for robust privacy frameworks, usage boundaries, and transparency before fully autonomous AI can be widely adopted.
This episode serves as a cautionary tale not just for ByteDance but for the global tech industry. Companies like Apple, Google, and OpenAI are all exploring AI agents capable of performing tasks autonomously, and the public’s trust will play a crucial role in determining adoption rates.
Global AI Competition and the Future of Mobile Agents
The race to develop advanced AI assistants extends far beyond China. OpenAI recently introduced the Shopping Research feature in ChatGPT, allowing users to visually compare products and make purchases, demonstrating a shift from question-answering to actionable, autonomous assistance. Similarly, Apple is reportedly developing an advanced AI suite for Siri, expected to launch globally in 2026, with assistance from Alibaba to bring features to China.
These developments suggest that AI agents capable of seeing, thinking, and acting on behalf of users could become the next major leap in mobile computing. The Nubia M153, while scaled back, offers a glimpse into a future where devices operate almost independently, executing complex tasks efficiently while anticipating user needs.
ByteDance’s Strategy and Market Implications
ByteDance’s AI phone initiative reflects its broader strategy to diversify beyond social media and content platforms. By integrating AI deeply into mobile hardware, the company positions itself to compete in a rapidly evolving AI ecosystem. The Nubia M153 could potentially set new benchmarks for AI assistants if privacy concerns are addressed effectively.
The Chinese smartphone market is highly competitive, with companies like Xiaomi, Huawei, and Oppo investing heavily in AI and smart devices. ByteDance’s early foray into fully agentic AI phones may give it a strategic advantage, provided it can reassure users about privacy and security. Regulatory approval, user trust, and responsible AI deployment will be key to the product’s success.
Lessons from the Nubia M153 Launch
Several lessons emerge from ByteDance’s brief experiment with a fully agentic AI phone:
- Innovation carries risks: Autonomous AI systems offer remarkable convenience but raise privacy and security challenges.
- User trust is crucial: Public perception and confidence are essential for adoption of advanced AI technologies.
- Regulation matters: Compliance with privacy regulations and transparent data handling are mandatory for sustainable AI deployment.
- Scaling cautiously: ByteDance’s decision to limit AI capabilities demonstrates the importance of phased rollouts for sensitive technology.
- Global AI race: Companies worldwide are striving to develop AI agents that go beyond traditional assistants, signaling a major shift in mobile computing.

Conclusion
The Nubia M153 AI smartphone represents a significant milestone in the evolution of mobile technology. By integrating a fully agentic AI capable of performing multi-step tasks autonomously, ByteDance has pushed the boundaries of what AI can do on personal devices. Yet, the swift response to privacy concerns underscores the delicate balance between innovation and user trust.
As AI agents continue to advance, the industry must navigate complex ethical, regulatory, and technical challenges. ByteDance’s experiment, even in its scaled-back form, serves as a glimpse into a future where smartphones may operate with near-human autonomy. For consumers, it highlights both the promise of convenience and the importance of vigilance in protecting personal data.
With companies like OpenAI, Apple, and Google also pushing the limits of autonomous AI, the next few years could redefine how humans interact with technology, making agentic AI an integral part of daily life. ByteDance’s Nubia M153 may not be fully realized yet, but it sets the stage for the AI-powered devices of tomorrow.
For continued updates on tech news and digital developments, visit our Tech News section and The News Update.